# Hot Reload
"Hot Reload" is not simply reloading the page when you edit a file. With hot reload enabled, when you edit a *.vue file, all instances of that component will be swapped in without reloading the page. It even preserves the current state of your app and these swapped components! This dramatically improves the development experience when you are tweaking the templates or styling of your components.
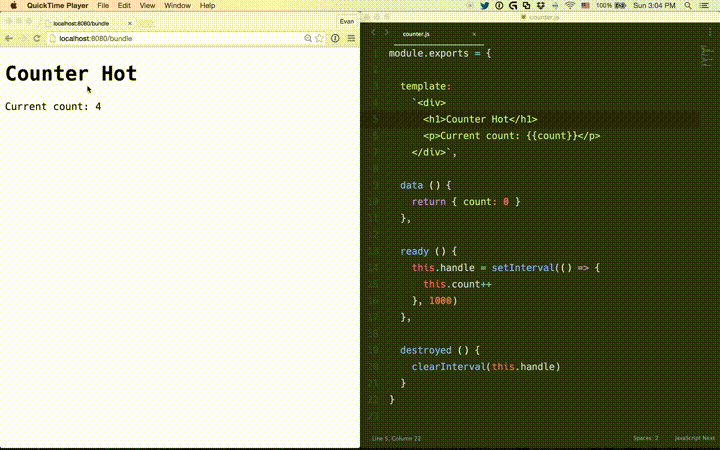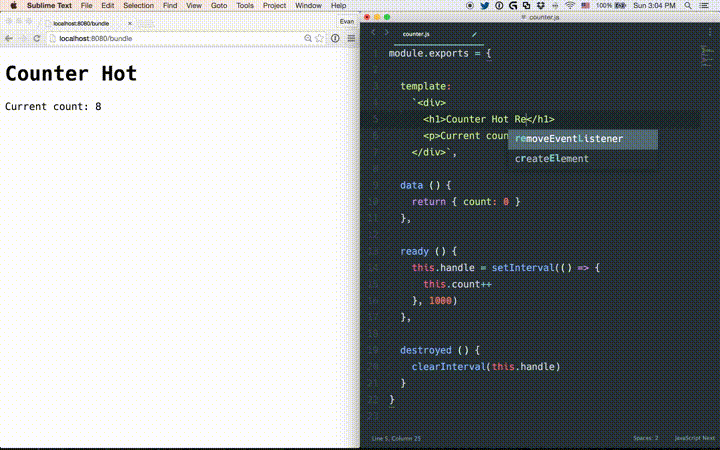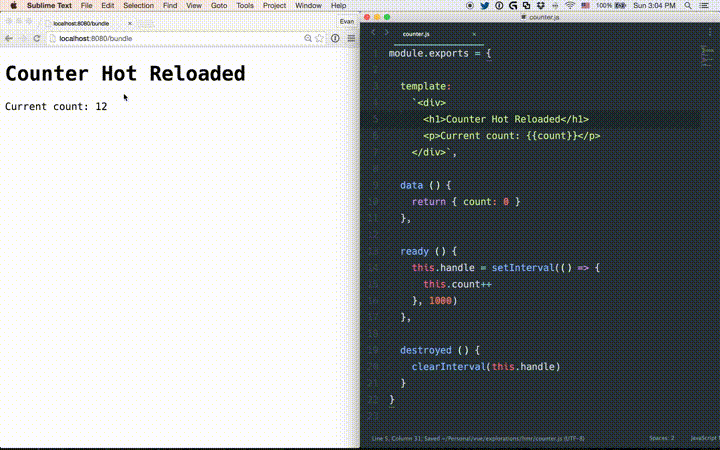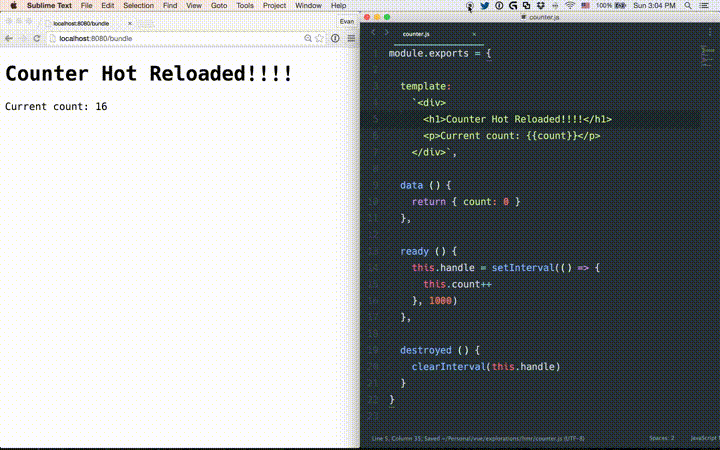
# State Preservation Rules
When editing the
<template>of a component, instances of the edited component will re-render in place, preserving all current private state. This is possible because templates are compiled into new render functions that produce no side-effects.When editing the
<script>part of a component, instances of the edited component will be destroyed and re-created in place. (State of the other components in the app are preserved) This is because<script>can include lifecycle hooks that may produce side-effects, so a "reload" instead of re-render is required to ensure consistent behavior. This also means you need to be careful about global side effects such as timers inside your components lifecycle hooks. Sometimes you may need to do a full-page reload if your component produces global side-effects.<style>hot reload operates on its own viavue-style-loader, so it doesn't affect application state.
# Usage
When scaffolding the project with vue-cli, Hot Reload is enabled out-of-the-box.
When manually setting up your project, hot-reload is enabled automatically when you serve your project with webpack-dev-server --hot.
Advanced users may want to check out vue-hot-reload-api, which is used internally by vue-loader.
# Disabling Hot Reload
Hot Reload is always enabled except following situations:
- webpack
targetisnode(SSR) - webpack minifies the code
process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
You may use hotReload: false option to disable the Hot Reload explicitly:
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: {
hotReload: false // disables Hot Reload
}
}
]
}